Professor Yi-Kuen Lee's MEMS/NEMS Group
Micro ElectroMechanical Systems (MEMS)
is one of the fastest growing research field all over the world [1,2]. Thanks
to the hard-working of many MEMS researchers all over the world, traditional
MEMS has moved from pure academic research field [3] into one mature technology
in industry [4]. Recently, MEMS research has gradually moved into two new
frontier areas: bio-MEMS
and Nano Electro-Mechanical System (NEMS). MEMS/NEMS has attracted researchers
from a variety of disciplines including mechanical engineering (fluid
mechanics, solid mechanics, heat transfer, manufacturing), electrical
engineering (solid-state electronics, integrated circuit engineering) and basic
science such as physics, chemistry and biology. At HKUST, our research projects
are currently focusing on micro/nanofluidics
(micro chaotic mixer, micro/nano electrokinetic flow) and bio-MEMS (micro/nano
capillary electrophoresis chip, micro electroporation chip, micro/nano bubble
actuator to enhance bio-reaction).

Cover page of 2011 Mar 21's
issue of Angewandte Chemie Intl.
Ed.
World's first superhydrophobic nanoflower surface
on silicon micro-post
arrays using MPCVD of carbon nanotube
(J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010)
Droplet
dynamics video on nanoflower

High-aspect ratio (max= 50:1)
sub-micron pillar array for electrophoresis of large DNA molecules. It is
fabricated by projection photolithography (stepper), ICP DRIE etching and
oxidation. See our paper published in J. Micromech. Microeng., 16(4),
699-707, 2006, for detailed info. Our work is cited by STS company's
Innovations Newsletter in Jun-July 2006.
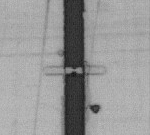
The micrograph of sub-micron bubble
actuator fabricated by projection photolithography (Stepper), etc.

Application Specific IC chip (0.35um
2P4M CMOS Technology) for mini/micro vibration power generator.

The time-periodic micro
cross-channel mixer.
References
|
3. R.P.
Feynman, There's
Plenty of Room at the Bottom, Caltech Engineering and Science, Feb, 1960
(JMEMS,
1(1), 60-66, 1992) |
|
4. Forbes magazine:Special issues on
micromachine, Apri 2 2001. |
|
5. K. Peterson,
Silicon as Mechanical Material, Proceedings of the IEEE,
70(5), 402-457, 1982 |
|
6. K. Najafi,
Micromachined Inertial Sensors, Proceedings of the IEEE,
86(8), 1640-1659, 1998. |
|
7. C. M. Ho & Y.
C. Tai, Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems and Fluid Flows, Ann.
Rev. of Fluid Mech., 30, 579-612, 1998. |
|
8. J. Voldman, et al.,
Microfabrication in Biology and Medicine, Annu.
Rev. Biomed. Eng., 1, 401-425, 1999. |
|
9.
D.L. Polla, et al., Microdevices in Medicines, Annu. Rev.
Biomed. Eng., 2, 551-576, 2000. |
|
10. H.G. Craighead, Nanoelectromechanical System, Science, Vol. 290, pp.
1532-1535, 2000. |
|
11. L. Bousse, et al.,
Electrokinetically Controlled Microfluidic Analysis Systems, Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol.
Struct., 29, 155-181, 2000. |
|
12. D.R.
Reyes, et al., Micrototal Analysis System. 1. Introduction, Theory and
Technology," Analytical Chemistry, 74(12) 2623-2636,
2002. |
|
13. P.-A. Auroux, et al., Micrototal
Analysis System. 2. Analytical Standard Operations and
Application," Analytical Chemistry, 74(12)
2637-2652, 2002. |
|
14. P.R.
Selvaganapath, el al., Recent Progress in Microfluidic Devices for Nucleic
Acid and Antibody Assay, Proceedings of IEEE,
91(6), 954-975, 2003. |
|
15. A. Ajdari, et al., Engineering Flow in
Small Devices: Microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip, Ann.
Rev. of Fluid Mech., 36,381-411, 2004. |
|
16. R.B. Fair, et al.,
Special issues on biomedical applications for MEMS and microfluidics, Proceedings of IEEE, 92(1), 3-5,
2004. |
|
17. R. Langer, et al., A
BioMEMS review: MEMS technology for physiologically integrated devices, Proceedings of IEEE,
92(1), 6-21, 2004. |
|
18. N. Li, A.
Tourovskaia, A. Floch,
Biology
on a Chip: Microfabrication for Studying the Behavior of Cultured Cells,
Critical Review in Biomedical Engineering, 31(5 & 6), 423-488, 2003 |
|
19. P. Tabeling, Introduction
to Microfluidics, |
|
20. H. Bruus, Theoretical
Microfluidics, |
|
21. J.C.T. Eijkel and
A. van den Berg, Nanofluidics: What is
it and what can we expect from it?, Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 1(3),
249-267, 2005. |
|
22. L. Chen, A. Manz
and P.J.R. Day, Total nucleic
acid analysis integraed on microfluidic devices, Lab on a Chip, 7,
1413-1423, 2007 |
|
23 C.D. Chin et al. "Lab-on-a-chip
devices for global health: Past studies and future", Lab on Chip, 7,
41-57, 2007. |
|
23. G.M. Whitesides, The origins and the future of
microfluidics, Nature, 442, 368-373, 2006 |
News:
Jun 2013: The project, "Intelligent Happiness
Detector," of three students (Yejun Zhu, Weiqiang Li, Yuanwu Chen)
supervised by Dr. Lee won the 3rd Prize
in the International Contest of Application in Nano-Micro Technology (iCAN 2013).
Mar 2012: M. Lee, Y.-K. Lee and Y. Zohar, "Single-phase liquid flow forced convection under nearly
uniform heat flux boundary condition in microchannels,” in Journal of
Micromechanics and Microengineering (JMM) (Vol. 22, No. 3, 035105, 2012) was chosen
as the Cover Page of Mar 2012 issue of JMM.
Mar 2011: S. Wang et al., “Highly Efficient Capture of
Circulating Tumor Cells Using Nanostructured Silicon Substrates with Integrated
Chaotic Micromixers,” (Angewandte Chemie International Ed., Vol.50
pp.3084-3088, 2011) was chosen as the Cover Page of Mar 21’s issue of
Angrew. Chem Int. Ed.. (in collaboration with Prof Hsian-Rong Tseng at
UCLA). This work was also featured in Nature
Medicine (Mar 2011 Issue).
Jan 2011: Our superhydrophobic nanoflower surfaces has been cited on
the website of The Chinese International NEMS Network and it is one of the most
frequently viewed article of the website (CINN), Selected videoclips
can be found on youtube.
More detailed info can be found on L. Chen, et al., “Static and Dynamic
Characterization of Robust Superhydrophobic Surfaces Built from Nano-flowers on
Silicon Micro-Post Arrays," Journal Micromechanics and
Microengineering, Vol. 20. No. 10, 105001 (8pp), 2010
Jan 2010: The students of Final Year Design Project (FYDP),
"Wireless Landslide Alert System for Slopes in Hong Kong Using MEMS Motion
Sensors," got the 2nd Prize (US$2,000) in iCAN 2009 (International Contest of Applications
in Nano/Micro Technologies) on 22 Jan 2010.
Oct 2009: Longquan's superhydrophobic abstract was accepted by IEEE
MEMS 2010, Jan 24-28,
2010.
Nov 2009: The book chapter, "Micro/Nanofluidic
Process," co-authored by Prof Patrick Tabeling at ESPCI and Dr.
Yi-Kuen Lee will be published by Oxford University Press in Feb 2010: Micro/Nano
Technology Systems for Biomedical Applications, edited by Prof Chih-Ming
Ho. The royalty of this book will be donated to SavetheChildren.org
Jun 2009: Dr Yun-Yang Ling's JM3 paper about
micro flow cytometer using giant electrorheological fluid (GER) was selected by
for the May
15, 2009 issue (Vol. 17, No. 10) of Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research (published
by the American Physical Society and American Institute of Physics).
--------------------------------------------------------
Prof. Yi-Kuen Lee's MEMS/NEMS
Group
Email to Webmaster
